


23/01/22
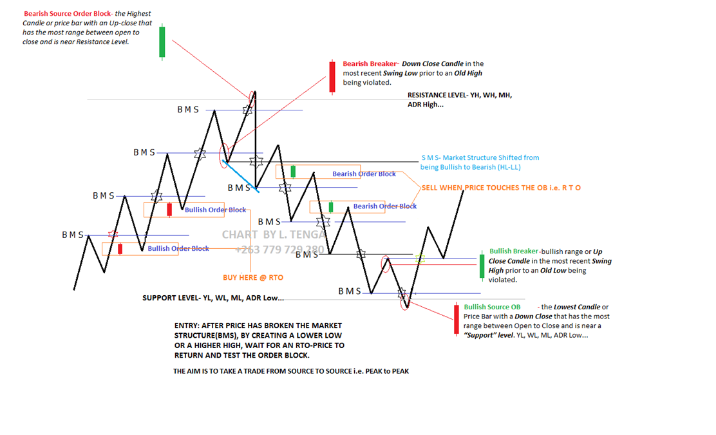
Institutions trade using order blocks.
The Order Block is a specific price range
or candle where institutions will be buying or selling againstb
theretail trend/dump money.
Institutions leave order blocks for themselves to trade at a later stage.
They will reverse the price to a previous order and
then driving the pricehard in the direction of the
trend(The real institutional trend).
These order blocks we can also call them specific levels of either going Long or Short.
If an order block is violated or broken, it now qualifies as a Breaker,
meaning Price will retest back to that
order block.
Sometimes we call it a failed order block.
NB:YOU DON’T TRADE ORDER BLOCKS STRAIGHTAWAY,
YOU WAIT FOR PRICE TO COME BACK
TO THAT ORDER BLOCK THEN YOU TAKE A TRADE.
23/01/22

Types of OBs:
i. Bullish Order Block (BUB)
ii. Bearish Order Block (BEB)
The Order of OBs
1. Source OB
2. Breaker OB
3. Continuation OB (Traditional/Basic OB)
Understanding Algorithmic Price Delivery
IPDA- Interbank Price Delivery Algorithm
OB-Order Block
FVG- Fair Value Gap
SMT- Smart Money
BiSi- Buy Side Imbalance Sell Side Inefficiency.
SiBi- Sell Side Imbalance Buy Side Inefficiency.
RjB- Rejection Block
RTO- Return to Order Block
RTF- Return to Fvg
BRK- Breaker
SOB- Source Order Block
BMS- Break of Market Structure
OTE- Optimum Trade Entry
23/01/22
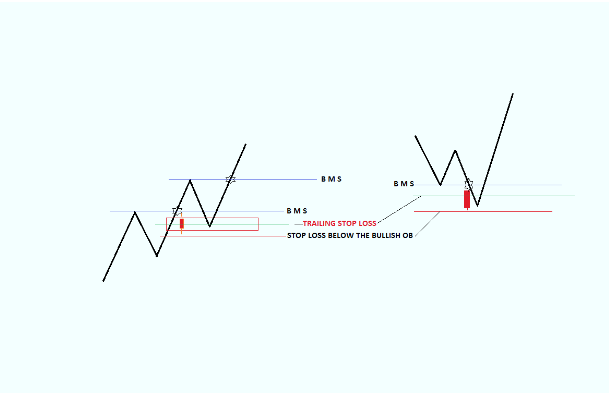
The Low of the Bullish OrderBlock
is the location of a relatively safe Stop Loss placement.
Just below the 50% of the OrderBlock
total range is also considered to be a good location
to raise the Stop Loss after Price runs away from
the Bullish OrderBlock to reduce Risk when applicable.